Introduction
In the world of fixed-income investments, understanding duration is crucial for managing interest rate risks. Among the various duration metrics, Macaulay Duration plays a pivotal role in assessing the time-weighted average maturity of a bond. Named after the economist Frederick Macaulay, this concept helps investors gauge the sensitivity of a bond’s price to interest rate fluctuations. This article explores Macaulay Duration in detail, covering its origin, formula, influencing factors, and practical insights.
What is Macaulay Duration?
Macaulay Duration represents the weighted average time an investor must wait to receive the bond’s cash flows (coupons and principal repayment). It is expressed in years and provides an estimate of when the investment is expected to be repaid. The higher the duration, the more sensitive the bond is to interest rate changes.

Origin of Macaulay Duration
Frederick Macaulay introduced the concept in 1938 to provide a more structured measure of bond duration. His research aimed at quantifying the relationship between bond prices and interest rate fluctuations, laying the foundation for modern bond valuation techniques.
Macaulay Duration Formula
The formula for Macaulay Duration is:
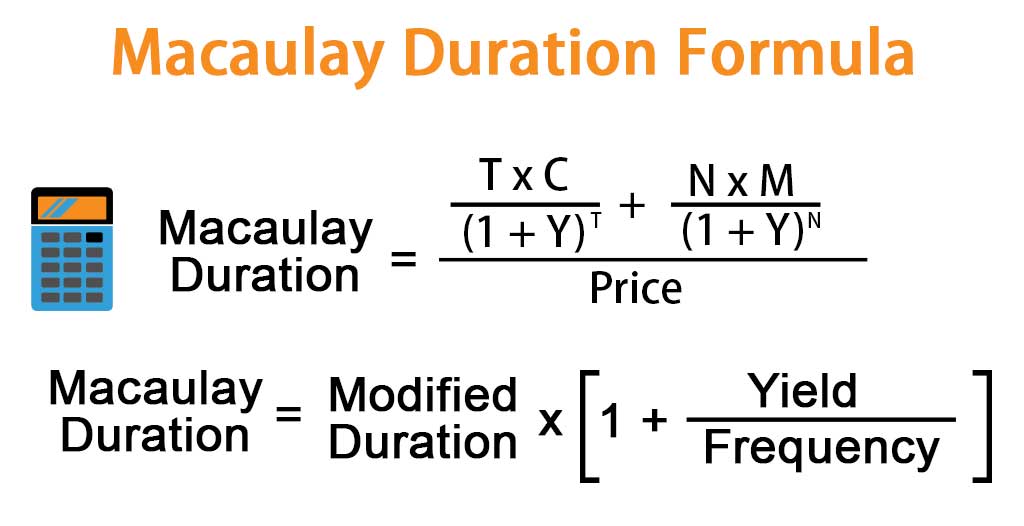
Where:
- T: Total Time Period
- C: Coupon Payment
- Y: Yield
- N: Total Number of Periods
- M: Maturity
- Price: Present Value of All the Cash Flows
Example Calculation
Consider a bond with:
- Face Value: ₹1,000
- Coupon Rate: 5% (annual)
- Maturity: 3 years
- Yield to Maturity: 6%
Step 1: Compute Present Value of Cash Flows
Yearly coupon = ₹50 (5% of ₹1,000) Discounting the cash flows:
- Year 1: 50/(1.06)1=47.1750 / (1.06)^1 = 47.17
- Year 2: 50/(1.06)2=44.5050 / (1.06)^2 = 44.50
- Year 3: (50+1000)/(1.06)3=839.62(50 + 1000) / (1.06)^3 = 839.62
Total Present Value (Bond Price) = ₹931.29
Step 2: Compute Weighted Sum
(47.17×1)+(44.50×2)+(839.62×3)=2855.04
Macaulay Duration = 2855.04 / 931.29 = 3.07 years
Factors Affecting Macaulay Duration
- Coupon Rate: Higher coupon payments lead to lower duration since investors recover their investment faster.
- Time to Maturity: Longer maturities generally result in higher durations.
- Yield to Maturity (YTM): Higher yields reduce duration as the present value of future cash flows declines.
- Frequency of Payments: More frequent coupon payments (semi-annual vs. annual) reduce Macaulay Duration.
Key Insights
- Macaulay Duration is best suited for fixed-income securities with regular coupon payments.
- It serves as a baseline for Modified Duration, which estimates bond price sensitivity to interest rate changes.
- Zero-coupon bonds have Macaulay Duration equal to their maturity since all cash flows are received at the end.
- Portfolio managers use it for immunization strategies to balance interest rate risk.
Conclusion
Macaulay Duration is a fundamental concept in bond valuation and risk management. It helps investors and analysts understand how bond prices will react to interest rate changes, aiding in portfolio decisions. While it provides a robust measure of bond duration, combining it with other duration metrics like Modified Duration and Effective Duration can enhance investment strategies.
Understanding and applying Macaulay Duration allows fixed-income investors to make informed decisions and navigate interest rate volatility effectively.
Discalimer!
The content provided in this blog article is for educational purposes only. The information presented here is based on the author's research, knowledge, and opinions at the time of writing. Readers are advised to use their discretion and judgment when applying the information from this article. The author and publisher do not assume any responsibility or liability for any consequences resulting from the use of the information provided herein. Additionally, images, content, and trademarks used in this article belong to their respective owners. No copyright infringement is intended on our part. If you believe that any material infringes upon your copyright, please contact us promptly for resolution.